3D printing is fundamentally a mechanism of creating solid three dimensional objects from blueprints of physical things in the form of digital files. It also has some other names like additive manufacturing, desktop fabrication, and prototyping process, etc. By using this technology we can create real objects from three-dimensional models. It is a contra process of subtractive manufacturing which involves cutting pieces of plastic or metals for milling machines.
Unlike a 2D inkjet printer a 3D printer prints a real 3-dimensional object layer by layer from the digital blueprint. We can see each layer of the object as horizontally cross-sectioned and delicately sliced. It facilitates you to build complex shaped objects, things, and parts by using less material and less effort than conventional procedures like formative manufacturing or subtractive machining. In this technology, no special tools are required. The part is created straight on to the built platform by layers. It has made so many things possible which were thought impossible in the past. It has widened the path of construction and creation of different objects and things of the real world.
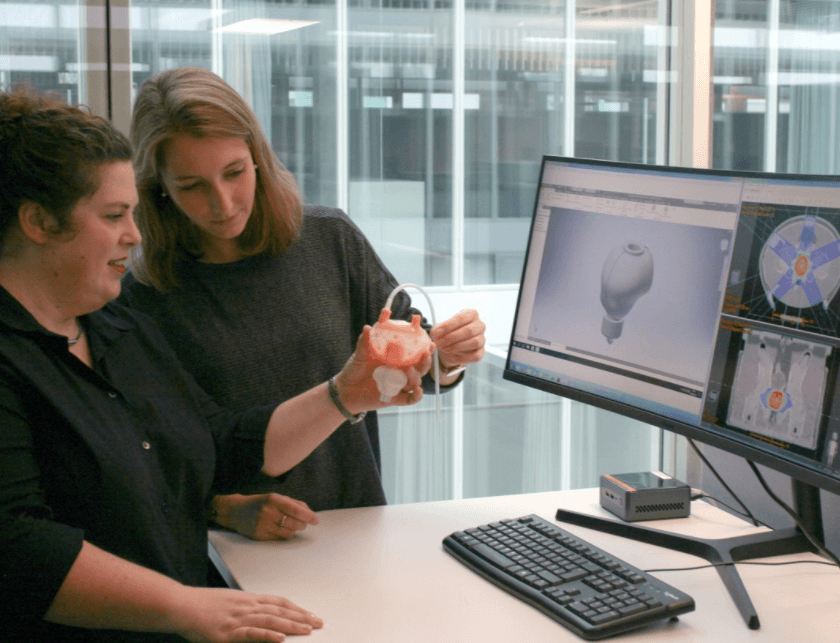
As the interest of the world is increasing in 3D printing service, it is widening day by day. Many amazing, interesting, and useful things are being created even for daily use by this cutting edge growing technology. The technique of 3D printing has many applications and can be applied in many more in the future. The latest applications of 3D technology are as follows. In aerospace, creating aircraft, in automotive, creating cars, in healthcare, organ transplant, prosthetic limbs, entertainment, robotics, design industry, education, fashion industry, construction niche, and food industry. Although 3D printing has brought a revolution in all the above-said fields Medical industry is one of the most important applications of 3D printing. Doctors can generate Patient-specific 3D body models of the patient’s body parts or organs. It can be helpful in different organs transplant.
There are various 3D printing technologies, different from each other. The basic difference between them is how layers are built to produce parts of the model. Names of some widely used 3D printing technologies are:
- FDM: Material Extrusion: Material is selectively distributed through a nozzle or orifice.
- BJ: Binder Jetting: Liquid bonding agent (LBA) very carefully binds particles of the powder bed.
- SLS, DMLS, and SLM: Powder Bed Fusion: A very high energy origin carefully fuses particles of powder.
- LENS, LBMD: Direct Energy Deposition: A very high energy source fuses substance as it is accumulated.
- SLA and DLP: Vat Polymerization: Liquid photopolymer in a vat is selectively cured employing UV light.
- UAM, LOM: Sheet Lamination: Sheets of material are formed layer by layer.
- MJ: Material Jetting: Droplets of material are carefully accumulated and treated.
3D printing is a very rapidly growing technology human is taking lots of advantages of this technology but it also comes with its limitations and still is behind from traditional printing in some fields. Here we shall discuss some pros and cons of 3D technology.

Advantages of 3D printing:
- No extra cost in Geometric complexity.
- Start-up costs are very low.
- Each part can be customized.
- Very rapid turnaround and so low-cost prototyping.
- A large range of materials can be used.
Limitations of 3D printing:
- Lower vitality and anisotropic material properties.
- Very expensive at higher volumes.
- Limited accuracy & endurance.
- Support removal and post-processing.
- Large time scale.


